Create and approve User and Functional requirements as part of an ALM Project.
Before you begin
You must be a member of the relevant Event or Task Assignment group or Assigned to user to perform these steps.
Procedure
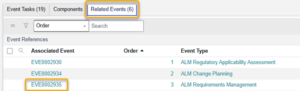
- Open the Requirements Management Event associated with the ALM Project.
- If the Requirements Management Event is in Triage, click Review Event Plan to move it to the Planning state. Ensure each step has an Assignment group and/or Assigned to user and click Start Work to move the Requirements Management Event to the In Progress state.
- Open the Create Requirements task and click Start Work to move the task to the In Progress state.
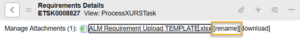
- Click the Download Requirement Template related link and fill out the template according to the instructions included in the file.
- Requirement Types:Parent, URS, FRS (Parent is a header/epic, not directly testable; URS/FRS are requirements and can be linked to test scripts.)
- Hierarchy Structure:Parent requirements can have children that are also Parent requirements. This allows for a multi-level hierarchy. Each parent should have at least one child.
- Drag and drop the completed file into the system or use the Manage Attachments (paper clip) button to upload. Once the file is attached, click Rename to ensure the filename is ‘ALM Requirement Upload TEMPLATE.xlsx’.
- Reload the form or click Save.
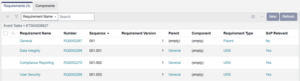
- Click Load Attached Requirementsto populate the Requirements related list (tab at the bottom of the form) based on the uploaded template.
Note: the system auto-generates the Sequence numbers based on the parent-child hiearchy, and these numbers will be updated automatically if requirements are added or deleted.
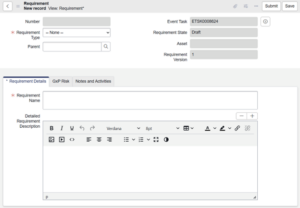
- You may also create a requirement directly by clicking New in the Requirements related list. Complete the fields on the form and click Submit to return to the list or Save to remain in the form.
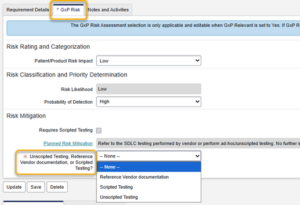
- For each requirement, specify how it will be tested or verified (Unscripted Testing, Reference Vendor Documentation, or Scripted Testing).
When deciding how to verify each requirement, consider the following factors:
- Risk and Impact:
- High-risk or critical features → Use scripted testingfor precise, repeatable checks and audit-ready evidence.
- Lower-risk features → Use unscripted testingfor flexible exploration with less documentation burden.
- Very low-risk, standardized functions → Use vendor documentationif reputable and robust.
- Requirement Clarity and Complexity:
- Clear, objective requirements → Best verified with scripted testinghaving defined pass/fail criteria.
- Subjective or exploratory requirements → Benefit from unscripted testingto uncover unexpected issues.
- Industry-standard or well-described vendor functions → Often verified by referencing vendor documentation.
- Regulatory or Compliance Needs:
- Regulation-related functionality (e.g., GxP) → May requirescripted testing for traceability and compliance.
- Non-regulated areas (e.g., cosmetic UI) → Can be handled by unscripted testing.
- Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software → May be verified through vendor documentationif supported by documented risk assessment.
Quick Decision Guide:
- High risk + clear requirement → Scripted testing
- Low risk + exploratory area → Unscripted testing
- Low risk + standard function → Vendor documentation
This quick decision guide is an example only—use discretion to ensure compliance, efficiency, and thorough coverage without unnecessary effort.
- Attempting to complete the task will prompt you if any mandatory fields were missed. Open the indicated requirements to complete the missing information (indicated by an asterisk *).
- Once all mandatory fields are completed for the task, click
Approving the Requirements
Once the Create Requirements task is completed, approval tasks for it will open. For guidance on how to approve or reject the task, see [[Approve or Reject a Task]].
Requirements Management Event Closure
When the final Approval task is Closed – Complete, the Requirements Management Event state changes to Closed.